---
title: Spring 资源管理
date: 2019-09-04 19:46:41
order: 20
categories:
- Java
- 框架
- Spring
- Spring核心
tags:
- Java
- 框架
- Spring
- Resource
permalink: /pages/926576ff/
---
# Spring 资源管理
> Version 6.0.3
## Resource 接口
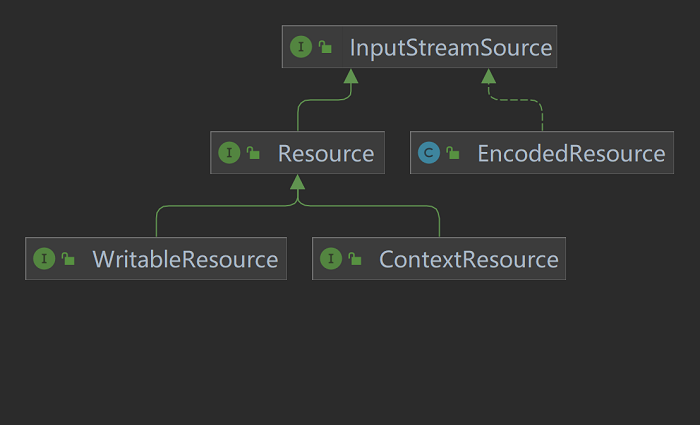
相对标准 URL 访问机制,Spring 的 `org.springframework.core.io.Resource` 接口抽象了对底层资源的访问接口,提供了一套更好的访问方式。
```java
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
boolean exists();
boolean isReadable();
boolean isOpen();
boolean isFile();
URL getURL() throws IOException;
URI getURI() throws IOException;
File getFile() throws IOException;
ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException;
long contentLength() throws IOException;
long lastModified() throws IOException;
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
}
```
正如 `Resource` 接口的定义所示,它扩展了 `InputStreamSource` 接口。`Resource` 最核心的方法如下:
- `getInputStream()` - 定位并且打开当前资源,返回当前资源的 `InputStream`。每次调用都会返回一个新的 `InputStream`。调用者需要负责关闭流。
- `exists()` - 判断当前资源是否真的存在。
- `isOpen()` - 判断当前资源是否是一个已打开的 `InputStream`。如果为 true,则 `InputStream` 不能被多次读取,必须只读取一次然后关闭以避免资源泄漏。对所有常用资源实现返回 false,`InputStreamResource` 除外。
- `getDescription()` - 返回当前资源的描述,当处理资源出错时,资源的描述会用于错误信息的输出。一般来说,资源的描述是一个完全限定的文件名称,或者是当前资源的真实 URL。
常见 Spring 资源接口:
| 类型 | 接口 |
| ---------- | ----------------------------------------------------- |
| 输入流 | `org.springframework.core.io.InputStreamSource` |
| 只读资源 | `org.springframework.core.io.Resource` |
| 可写资源 | `org.springframework.core.io.WritableResource` |
| 编码资源 | `org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource` |
| 上下文资源 | `org.springframework.core.io.ContextResource` |
## 内置的 Resource 实现
Spring 包括几个内置的 Resource 实现:
| 资源来源 | 前缀 | 说明 |
| ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| [`UrlResource`](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#resources-implementations-urlresource) | `file:`、`https:`、`ftp:` 等 | `UrlResource` 封装了一个 `java.net.URL` 对象,**用于访问可通过 URL 访问的任何对象**,例如文件、HTTPS 目标、FTP 目标等。所有 URL 都可以通过标准化的字符串形式表示,因此可以使用适当的标准化前缀来指示一种 URL 类型与另一种 URL 类型的区别。 这包括:`file`:用于访问文件系统路径;`https`:用于通过 HTTPS 协议访问资源;`ftp`:用于通过 FTP 访问资源等等。 |
| [`ClassPathResource`](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#resources-implementations-classpathresource) | `classpath:` | `ClassPathResource` **从类路径上加载资源**。它使用线程上下文加载器、给定的类加载器或指定的 class 类型中的任意一个来加载资源。 |
| [`FileSystemResource`](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#resources-implementations-filesystemresource) | `file:` | `FileSystemResource` **是 `java.io.File` 的资源实现**。它还支持 `java.nio.file.Path` ,应用 Spring 的标准对字符串路径进行转换。`FileSystemResource` 支持解析为文件和 URL。 |
| [`PathResource`](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#resources-implementations-pathresource) | 无 | `PathResource` 是 `java.nio.file.Path` 的资源实现。 |
| [`ServletContextResource`](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#resources-implementations-servletcontextresource) | 无 | `ServletContextResource` **是 `ServletContext` 的资源实现**。它表示相应 Web 应用程序根目录中的相对路径。 |
| [`InputStreamResource`](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#resources-implementations-inputstreamresource) | 无 | `InputStreamResource` **是指定 `InputStream` 的资源实现**。注意:如果该 `InputStream` 已被打开,则不可以多次读取该流。 |
| [`ByteArrayResource`](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#resources-implementations-bytearrayresource) | 无 | `ByteArrayResource` 是指定的二进制数组的资源实现。它会为给定的字节数组创建一个 `ByteArrayInputStream`。 |
## ResourceLoader 接口
`ResourceLoader` 接口用于加载 `Resource` 对象。其定义如下:
```java
public interface ResourceLoader {
Resource getResource(String location);
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
```
Spring 中主要的 ResourceLoader 实现:
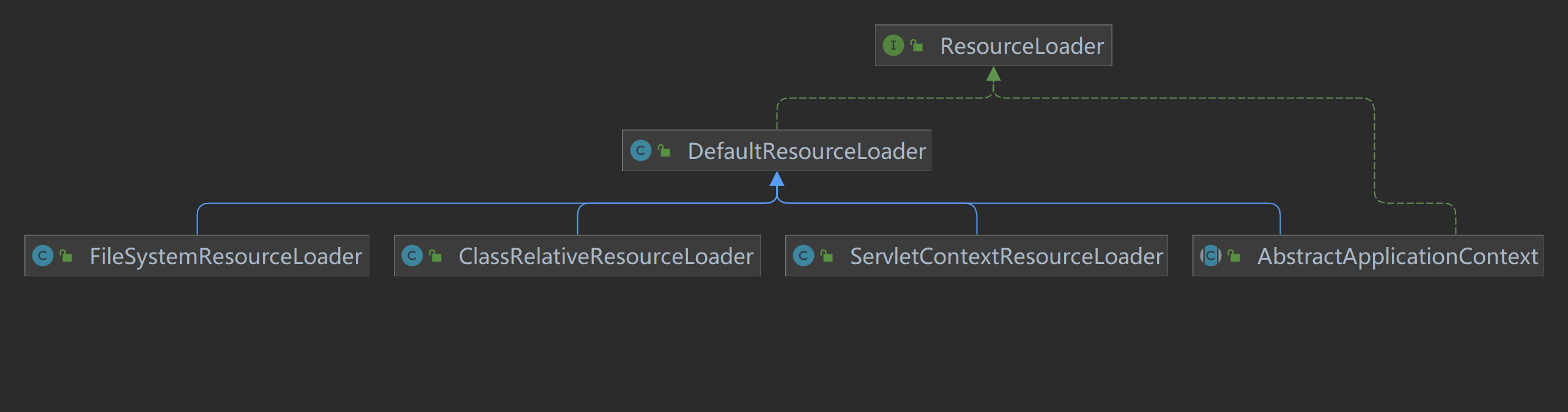
Spring 中,所有的 `ApplicationContext` 都实现了 `ResourceLoader` 接口。因此,所有 `ApplicationContext` 都可以通过 `getResource()` 方法获取 `Resource` 实例。
【示例】
```java
// 如果没有指定资源前缀,Spring 会尝试返回合适的资源
Resource template = ctx.getResource("some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
// 如果指定 classpath: 前缀,Spring 会强制使用 ClassPathResource
Resource template = ctx.getResource("classpath:some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
// 如果指定 file:、http 等 URL 前缀,Spring 会强制使用 UrlResource
Resource template = ctx.getResource("file:///some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
Resource template = ctx.getResource("http://myhost.com/resource/path/myTemplate.txt");
```
下表列举了 Spring 根据各种位置路径加载资源的策略:
| 前缀 | 样例 | 说明 |
| ------------ | -------------------------------- | :----------------------------------- |
| `classpath:` | `classpath:com/myapp/config.xml` | 从类路径加载 |
| `file:` | `file:///data/config.xml` | 以 URL 形式从文件系统加载 |
| `http:` | `http://myserver/logo.png` | 以 URL 形式加载 |
| 无 | `/data/config.xml` | 由底层的 ApplicationContext 实现决定 |
## ResourcePatternResolver 接口
`ResourcePatternResolver` 接口是 `ResourceLoader` 接口的扩展,它的作用是定义策略,根据位置模式解析 `Resource` 对象。
```java
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
```
`PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver` 是一个独立的实现,可以在 `ApplicationContext` 之外使用,也可以被 `ResourceArrayPropertyEditor` 用于填充 `Resource[]` bean 属性。`PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver` 能够将指定的资源位置路径解析为一个或多个匹配的 `Resource` 对象。
> 注意:任何标准 `ApplicationContext` 中的默认 `ResourceLoader` 实际上是 `PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver` 的一个实例,它实现了 `ResourcePatternResolver` 接口。
## ResourceLoaderAware 接口
`ResourceLoaderAware` 接口是一个特殊的回调接口,用来标记提供 `ResourceLoader` 引用的对象。`ResourceLoaderAware` 接口定义如下:
```java
public interface ResourceLoaderAware {
void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader);
}
```
当一个类实现 `ResourceLoaderAware` 并部署到应用程序上下文中(作为 Spring 管理的 bean)时,它会被应用程序上下文识别为 `ResourceLoaderAware`,然后,应用程序上下文会调用 `setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader)`,将自身作为参数提供(请记住,Spring 中的所有应用程序上下文都实现 `ResourceLoader` 接口)。
由于 `ApplicationContext` 是一个 `ResourceLoader`,该 bean 还可以实现 `ApplicationContextAware` 接口并直接使用提供的应用程序上下文来加载资源。 但是,一般来说,如果您只需要这些,最好使用专门的 `ResourceLoader` 接口。 该代码将仅耦合到资源加载接口(可以被视为实用程序接口),而不耦合到整个 Spring `ApplicationContext` 接口。
在应用程序中,还可以使用 `ResourceLoader` 的自动装配作为实现 `ResourceLoaderAware` 接口的替代方法。传统的构造函数和 `byType` 自动装配模式能够分别为构造函数参数或 setter 方法参数提供 `ResourceLoader`。 为了获得更大的灵活性(包括自动装配字段和多参数方法的能力),请考虑使用基于注解的自动装配功能。 在这种情况下,`ResourceLoader` 会自动连接到需要 `ResourceLoader` 类型的字段、构造函数参数或方法参数中,只要相关字段、构造函数或方法带有 `@Autowired` 注解即可。
## 资源依赖
如果 bean 本身要通过某种动态过程来确定和提供资源路径,那么 bean 可以使用 `ResourceLoader` 或 `ResourcePatternResolver` 接口来加载资源。 例如,考虑加载某种模板,其中所需的特定资源取决于用户的角色。 如果资源是静态的,完全消除 `ResourceLoader` 接口(或 `ResourcePatternResolver` 接口)的使用,让 bean 公开它需要的 `Resource` 属性,并期望将它们注入其中是有意义的。
使注入这些属性变得简单的原因是所有应用程序上下文都注册并使用一个特殊的 JavaBeans `PropertyEditor`,它可以将 `String` 路径转换为 `Resource` 对象。 例如,下面的 MyBean 类有一个 `Resource` 类型的模板属性。
【示例】
```xml
<bean id="myBean" class="example.MyBean">
<property name="template" value="some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt"/>
</bean>
```
请注意,配置中引用的模板资源路径没有前缀,因为应用程序上下文本身将用作 `ResourceLoader`,资源本身将根据需要通过 `ClassPathResource`,`FileSystemResource` 或 ServletContextResource 加载,具体取决于上下文的确切类型。
如果需要强制使用特定的资源类型,则可以使用前缀。 以下两个示例显示如何强制使用 `ClassPathResource` 和 `UrlResource`(后者用于访问文件系统文件)。
```xml
<property name="template" value="classpath:some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt">
<property name="template" value="file:///some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt"/>
```
可以通过 `@Value` 注解加载资源文件 `myTemplate.txt`,示例如下:
```java
@Component
public class MyBean {
private final Resource template;
public MyBean(@Value("${template.path}") Resource template) {
this.template = template;
}
// ...
}
```
Spring 的 `PropertyEditor` 会根据资源文件的路径字符串,加载 `Resource` 对象,并将其注入到 MyBean 的构造方法。
如果想要加载多个资源文件,可以使用 `classpath*:` 前缀,例如:`classpath*:/config/templates/*.txt`。
```java
@Component
public class MyBean {
private final Resource[] templates;
public MyBean(@Value("${templates.path}") Resource[] templates) {
this.templates = templates;
}
// ...
}
```
## 应用上下文和资源路径
### 构造应用上下文
应用上下文构造函数(针对特定的应用上下文类型)通常将字符串或字符串数组作为资源的位置路径,例如构成上下文定义的 XML 文件。
【示例】
```java
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("conf/appContext.xml");
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("conf/appContext.xml");
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:conf/appContext.xml");
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
new String[] {"services.xml", "daos.xml"}, MessengerService.class);
```
### 使用通配符构造应用上下文
ApplicationContext 构造器的中的资源路径可以是单一的路径(即一对一地映射到目标资源);也可以是通配符形式——可包含 classpath\*:也可以是前缀或 ant 风格的正则表达式(使用 spring 的 PathMatcher 来匹配)。
示例:
```java
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath*:conf/appContext.xml");
```
使用 `classpath*` 表示类路径下所有匹配文件名称的资源都会被获取(本质上就是调用了 ClassLoader.getResources(…) 方法),接着将获取到的资源组装成最终的应用上下文。
在位置路径的其余部分,`classpath*:` 前缀可以与 PathMatcher 结合使用,如:`classpath*:META-INF/*-beans.xml`。
## 问题
Spring 配置资源中有哪些常见类型?
- XML 资源
- Properties 资源
- YAML 资源
## 参考资料
- [Spring 官方文档之 Core Technologies](https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/core.html#beans)
- [《小马哥讲 Spring 核心编程思想》](https://time.geekbang.org/course/intro/265)