2021 fall, Financial-Engineering
Sangmin Lee (이상민)
According to Black-Scholes, we can hedge a call option whose pay-off diagram is max(S-K,0) and a put option whose max(K-S,0). We can also hedge a financial derivative which is made of call and put options with their help. But Black-Sholes cannot hedge all financial derivatives. Because they use the way called delta hedging, They can only predict the financial derivative based on call and put option. We want to solve this problem by using Neural Network and we call this solution Deep Hedging. The idea is Neural Network induces the proper delta. But, can Neural Network find the delta? To answer this, I’ll show followings: First, you can hedge an option by using Neural Network without Black-Sholes formula. And then, you can also hedge a financial derivative(option strategy) which is composed of call and put options. Second, I’ll drive a premium, which is the price of an option or a financial derivative. if we success above, we claim Neural Network can find the delta and thus I suggest that with Deep Hedging you can hedge any option strategies that have any pay-off, which is Black-Sholes can’t hedge. Then, the problem is how Neural Network can find the best hedging delta. We think that you can solve this problem with Recurrent Neural Network(RNN). The RNN store all previous data, so you can use this to find the delta, considering the previous all stock prices.
The first is what the Black-Sholes Option Pricing Formula is. We start with the binomial option pricing formula. They assume that there is no arbitrage, the interest rate is constant and the stock price follows a multiplicative binomial process over discrete periods. The rate of return on the stock over each period can have two possible values: u- 1 with probability q, or d - 1 with probability 1-q. Thus, if the current stock price is S, the stock price at the end of the period will be either uS or dS.
Let C be the current value of the call, C_u be its value at the end of the period if the stock price goes to uS, that is, (1) and C_d be its value at the end of the period if the stock price goes to dS, that is, (2). if there is now only one period remaining in the life of the call, we know that the terms of its contract and a rational exercise policy imply that Cu = max[0, uS-K] and Cd = max[0, dS –K].
Suppose we form a portfolio containing
Since we can select ∆ and B in any way we wish, suppose we choose them to equate the end-of-period values of the portfolio and the call for each possible outcome. This requires that (3) must be equal to (5) and (4) must be equal to (6).
Solving these equations, we find
With ∆ and B chosen in this way, we will call this the hedging portfolio. That is, if we have the delta stocks, we hedge the option. In general, Option pricing formula is
Delta, which is the number of stocks we have, is
By using these, the option price for Call is $$ C_{call} = SN(d_1) - K e^{-rt} N(d2) \quad \cdots \quad (8)$$ and for Put $$ C_{put} = K e{-rt} N(-d2) -SN(-d_1) \quad \cdots \quad (9)$$
So, if we know stock price, delivery price, remaining periods before its expiration date, volatility and interest rate, we can drive a option price.
The stock price is predicted as
$$ S_{t+\Delta t} = S_t(1+N(r\Delta t, \sigma^2 \Delta t^2))\quad \cdots \quad (10)$$
Note that
Then, the day cost for hedging is that the product of displacement of delta and stock price at that time. So, the total cost is just sum of the day costs. We call this cost the hedging cost. And it can be represented as
Suppose you sell an option and you want to hedge this. Then, you can get help from Black-Sholes. For example, let you sell a call option. All you have to do is just to calculate delta by using (8). Or a put option, (9). you hedge the option if and only If you have the same number of stock as delta. Because we suppose there is no arbitrage, the sum of the cost that you spend while hedging the option and pay-off of the option must be same as the option’s premium. Then, how can we hedge the option strategy that can’t get help from Black-Sholes? This is the reason why we suggest the Deep Hedging.
We want to make a neural network regress to the hedging delta. Let’s start with option hedging. For simplicity, let you sell a call option and hedge this. And suppose that interest rate, volatility is constant and equal to 0, 0.2 respectively. Let current stock price S0 be 1.00, delivery price K 1.00, remaining periods before its expiration date 30/365. Then according to (10), we can make scenarios that represent the stock price through time and let this S. Also, we can calculate the option price by (7), or directly (8) and (9). Before using neural network, check the Black-Sholes’ delta is valid. If we hedge the option with Black-Sholes, the sum of the hedging cost, pay-off and premium must be zero. The results are:
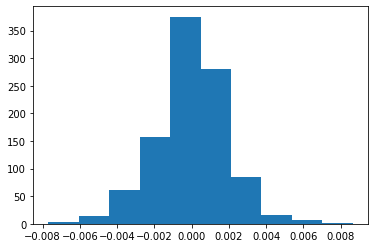
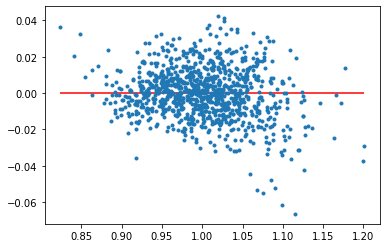
Fig.1 - Delta Hedging; Histogram(left) and Scatter plot(right)
From the results in Figure 1(left) and Figure 1(right), we may think the Black-Sholes formula is valid. Next is to find delta with neural network.
Let S be stock price scenarios and y be option price with Black-Sholes. Using these, we try hedging the option. if the sum of cost hedging the option, pay-off and premium driven by Black-Sholes is zero, we consider the delta neural network got as one Black-Sholes got. Then, this tell us we can hedge the option with that delta neural network get. Train the neural network. Inputs are Stock price scenarios, hedging cost initialized with zero and premium. And our targets(or labels) are zero. ; they must be zero since we want to hedge the option in no arbitrage world.
Fig.2 - Deep Hedging for a call; Histogram(left) and Scatter plot(right)
Figure 2(left) is a histogram whose x-axis is the values our neural network model put out and they represent the sum of hedging cost, pay-off and premium. if the neural network model is perfect and ideal, the values are all zero and the grap shows the Dirac delta function at zero. The result in Figure 1 is similar to a normal distribution(or a bell curve) and its mean is zero. Figure 2(right) is a scatter plot whose x-axis is delivery price and y-axis is the values our neural network model put out. if the neural network model is perfect and ideal, the graph is constant, that is, horizontal line equal to zero. From these results, we may think the neural network can find the hedging delta. To be more complicated, we try to hedge a financial derivative(option strategy) composed of call and put. We consider an iron condor. The iron condor is an options strategy consisting of two puts (one long and one short) and two calls (one long and one short), and four strike prices, all with the same expiration date. The iron condor earns the maximum profit when the underlying asset closes between the middle strike prices at expiration. In other words, the goal is to profit from low volatility in the underlying asset. The iron condor’s pay-off is, for example,
Fig.3 Iron Condor payoff’s shape
Important is the shape, not the specific values. In this case, we take the delivery prices as 90, 95, 105, 110. To hedge Iron condor, we need to make above payoff. For convenience, let delivery prices be 0.9, 0.95, 1.05, 1.10. By using four options, we make this. We try three cases whose components are different. One is to use only call, another is to use only put and the other is two calls and two puts.
The first is to use only call. To make above payoff, we must take two long positions to call and two short. Likewise, we put in the sum of Stock price sets, hedging cost initialized with zero and premium to neural network. our targets are zero. we use the same delta model to each three cases and the results are
Fig.4 Deep Hedging for a Iron Condor with 4 calls
The second is to use only put.
Fig.5 Deep Hedging for a Iron Condor with 4 puts
The last is to use two puts and two calls.
Fig.6 Deep Hedging for a Iron Condor with 2 puts and 2 calls
where the red lines are ideal cases of each. Among the results, using puts and calls is best, showing the lowest hedging error. (Compare the result in Figure 6 to in Figure 4,5)
From the above, you may think neural network can find the delta, hedging options or financial derivatives. Moreover, we suggest that neural network can find the hedging delta for any financial derivatives whose pay-off diagram is any functions so that Black-Sholes cannot do anything for those, although the better neural network must be needed. We call this Deep Hedging and suggest that the RNN is one of the solutions for better neural network. Before the next step, we should modify our model from the above, specifically inputs and outputs. And we introduce you the RNN. Note that we want to get the delta for hedging. if we put the stock price sets and pay-off into the neural network model, then we expect that neural network put out the premium, calculating the proper delta for hedging. Check this. For simplicity, use a call option. Inputs are the stock price sets and pay-off of call and target is premium of call.
We already know the premium of call from Black-Sholes, which is about 0.02. So we conclude our model works the same as we expected. So, we can hedge any option strategies as neural network calculate the delta for given premium. Then, the remaining problem is how we model a better neural network.
I try using GRU for deep hedging. For simplicity, we predict call’s delta at first. We put the stock price sets and pay-off in the GRU model. We expect that our model put out the premium of the call. So target(label) is the premium of the call and we give this with Black-Sholes.
We may think the RNNs model find the delta. But comparing these results to above results without RNNs, there is no dramatic improvement. But, I suggest that if you get more complex and well-made RNN model, you can hedge any kind of option strategies.